- Tầm quan trọng của nước đối với sức khỏe

Hình 1: Tác dụng của nước đối với cơ thể (Nguồn: [1]). Designer: Trương Tài Nhân
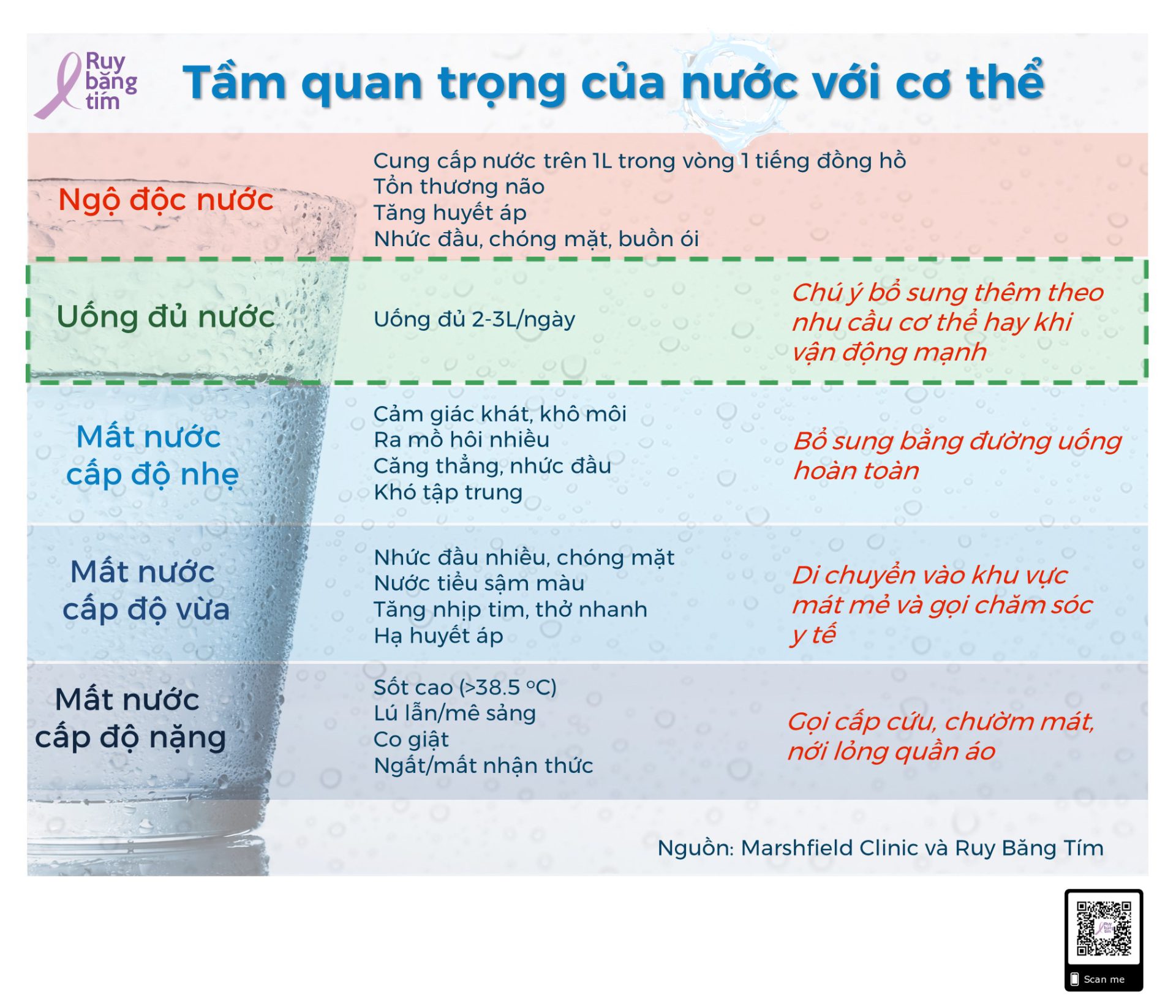
Do các vai trò trên, hằng ngày cần phải bổ sung nước đầy đủ cho lượng nước chúng ta mất đi thông qua vận động và sinh hoạt. Các phần sau sẽ giúp giải thích rõ hơn về tầm quan trọng của nước trong cơ thể của chúng ta.- Mất nước ảnh hưởng tới hoạt động của não bộ
- Uống đủ nước có thể phòng chống một số vấn đề sức khỏe
- Nên uống nước thế nào là đúng và đủ?
Bảng 1: Lượng nước xấp xỉ trong một số loại thực phẩm [23]
| % | Thực phẩm |
| 100% | Nước |
| 90–99% | Sữa không béo, dưa lưới, dâu tây, dưa hấu, rau diếp, bắp cải, cần tây, rau chân vịt |
| 80–89% | Nước trái cây, yogurt, táo, nho, cam, cà rốt, bông cải xanh, lê, dứa |
| 70–79% | Chuối, bơ, khoai tây hầm, bắp ngô luộc, tôm |
| 60–69% | Pasta, đậu, cá hồi, kem, ức gà |
| 50–59% | Thịt bò, thịt bít tết |
| 40–49% | Pizza |
| 30–39% | Phô mai, bánh mì |
| 20–29% | Xúc xích, bánh ngọt, bánh quy |
| 10–19% | Bơ, magarine, nho khô |
| 1–9% | Các loại hạt, bánh khô, ngũ cốc khô, bơ đậu phộng |
| 0% | Dầu ăn, đường tinh luyện |
- Uống nước đầy đủ bảo vệ sức khỏe nói chung. Đối với bệnh ung thư, chưa có sự liên hệ rõ ràng.
- Để đảm bảo đủ lượng nước hằng ngày, cần uống khoảng từ 2-3L nước và tăng lên nếu vận động nhiều, mất nhiều mồ hôi do thời tiết nóng hoặc cơ thể trong tình trạng bệnh lý.
- Nước uống tinh khiết (nước đã qua xử lý, nước đun sôi để nguội) là lựa chọn an toàn và kinh tế nhất để đảm bảo lượng này.
Tài liệu tham khảo
[2] Armstrong, L. E., Ganio, M. S., Casa, D. J., Lee, E. C., Mcdermott, B. P., Klau, J. F., . . . Lieberman, H. R. (2011). Mild Dehydration Affects Mood in Healthy Young Women. The Journal of Nutrition, 142(2), 382-388. doi:10.3945/jn.111.142000
[3] Ganio MS, Armstrong LE, Casa DJ, McDermott BP, Lee EC, Yamamoto LM, Marzano S, Lopez RM, Jimenez L, Le BL, Chevillotte E, Lieberman HR. (2011) Mild dehydration impairs cognitive performance and mood of men. Br.J.Nutr. 106:1535-1543
[4] Gopinathan, P. M., Pichan, G., & Sharma, V. M. (1988). Role of Dehydration in Heat Stress-Induced Variations in Mental Performance. Archives of Environmental Health: An International Journal, 43(1), 15-17. doi:10.1080/00039896.1988.9934367
[5] Cian, C., Barraud, P., Melin, B., & Raphel, C. (2001). Effects of fluid ingestion on cognitive function after heat stress or exercise-induced dehydration. International Journal of Psychophysiology, 42(3), 243-251. doi:10.1016/s0167-8760(01)00142-8
[6] Sharma VM, Sridharan K, Pichan G, Panwar MR. (1986) Influence of heat-stress induced dehydration on mental functions. Ergonomics 29:791-799
[7] Ely BR, Sollanek KJ, Cheuvront SN, Lieberman HR, Kenefick RW. (2013) Hypohydration and acute thermal stress affect mood state but not cognition or dynamic postural balance. Eur.J.Appl.Physiol 113:1027-1034
[8] Francesconi RP, Sawka MN, Hubbard RW & Pandolf KB (1989): Hormonal regulation of fluid and electrolytes: effects of heat exposure and exercise in the heat. In: Hormonal regulation of fluid and electrolytes. ed. JR Claybaugh & CE Wade, pp 45–85. New York and London: Plenum Press
[9] https://www.hormone.org/hormones-and-health/hormones/cortisol Truy cập ngày 17/7/2019
[10] Vedhara K, Hyde J, Gilchrist ID, Tytherleigh M & Plummer S (2000): Acute stress, memory, attention and cortisol. Psychoneuroendocrinology 25, 535–549
[11] Ciriello J, Hochstenbach SL & Pastor Solano-Flores L (1996): Changes in NADPH diaphorase activity in forebrain structures of the laminae terminalis after chronic dehydration
[12] Häussinger D, Roth E, Lang F & Gerok W (1993): Cellular hydration state: an important determinant of protein catabolism in health and disease. Lancet 341, 1330–1332
[13] Arnaud, M. J. (2003). Mild dehydration: a risk factor of constipation? European Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 57(S2), S88-S95. doi:10.1038/sj.ejcn.1601907
[14] https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/urologic-diseases/kidney-stone Truy cập ngày 17/7/2019
[15] https://www.nkfs.org/kidney-disease/common-kidney-disease/kidney-stones/ Truy cập ngày 17/7/2019
[16] Lubin F., Rozen P., Arieli B., Farbstein M., Knaani Y., Bat L., Farbstein H. (1997) Nutritional and lifestyle habits and water-fiber interaction in colorectal adenoma etiology. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 1997 Feb;6(2):79-85.
[17] Shannon J, White E, Shattuck AL, Potter JD. (1996) Relationship of food groups and water intake to colon cancer risk. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 1996 Jul;5(7):495-502.
[18] Michaud, D., Spiegelman, D., Clinton, S., Rimm, E., Curhan, G., Willett, W., Giovannucci, E. (1999) Fluid Intake and the Risk of Bladder Cancer in Men. N Engl J Med 1999; 340:1390-1397
DOI: 10.1056/NEJM199905063401803
[19] Bai Y, Yuan H, Li J, Tang Y, Pu C, Han P. (2014) Relationship between bladder cancer and total fluid intake: a meta-analysis of epidemiological evidence. World J Surg Oncol. 2014 Jul 17;12:223. doi: 10.1186/1477-7819-12-223.
[20] Michaud DS, Kogevinas M, Cantor KP, Villanueva CM, Garcia-Closas M, Rothman N, Malats N, Real FX, Serra C, Garcia-Closas R, Tardon A, Carrato A, Dosemeci M, Silverman DT. (2007) Total fluid and water consumption and the joint effect of exposure to disinfection by-products on risk of bladder cancer. Environ Health Perspect. 2007 Nov;115(11):1569-72.
[21] Jimenez, B., Richardot P., Picard P., Lepicard EM., De Meo M., Talaska G..
(2015) Effect of Increased Water Intake on Urinary DNA Adduct Levels and Mutagenicity in Smokers: A Randomized Study. Dis Markers. 2015;2015:478150. doi: 10.1155/2015/478150. Epub 2015 Aug 18.
[22] Popkin, B., D’Anci, KE. Rosenberg., IR (2010). Water, Hydration and Health. Nutr Rev. Aug; 68(8): 439–458.
[23] National Academies of Sciences, Engineering and Medicine. Dietary Reference Intakes: Water, Potassium, Sodium, Chloride, and Sulfate. Truy cập ngày 11/7/2019
[24] Stachenfeld NS, DiPietro L, Nadel ER, Mack GW. (1997) Mechanism of attenuated thirst in aging: role of central volume receptors. Am J Physiol. 1997 Jan;272(1 Pt 2):R148-57.
[25] Verbalis JG, Goldsmith SR, Greenberg A, Schrier RW, Sterns RH. (2007) Hyponatremia treatment guidelines 2007: expert panel recommendations. Am J Med. 2007 Nov;120(11 Suppl 1):S1-21.
[26] Almond CS, Shin AY, Fortescue EB, Mannix RC, Wypij D, Binstadt BA, Duncan CN, Olson DP, Salerno AE, Newburger JW, Greenes DS. (2005) Hyponatremia among runners in the Boston Marathon. N Engl J Med. 2005 Apr 14;352(15):1550-6.






